

Example #4Ĭode: print("Program with not equal to operator in Python 2.7 version") Now let us see the demonstration in the below example with the error that displays when the not equal to the operator in the program instead of ( != ). But this operator is not supported in the latest version as well as Python 3, and the above version also does not support it. In Python, the older versions had another operator for comparing the not equal to the operator, which is denoted as ( ). In Python, the not equal to the operator is denoted by (!=) and is more recommended by developers and is supported by Python 2 and 3 versions. This result can be seen in the above screenshot. So if this expression is satisfying, then it will print “not equal” else, if the expression is not satisfying, then it will print “equal”. In the program, we can see the expression given in the “ if ” condition using “is not” for comparing the values of the given operand with the value specified in the expression inside the if loop. Then we are trying to check if x value “is not” equal to 7. In the above program, we can see that we have declared only one operand x with the value as 5. Let us demonstrate below with an example. In Python, when we are using not equal to operator, then we have to note that the two operands that are declared must be of the same data type else in Python, if both the operands have different data types, then it will return not equal. To see the above program to have the output as “False”, then we need to define the values of two operands x and y with the same value. We can see we are trying to print the result of the expression x != y, which will print “True” as both the given operands are not equal. In the above program, we can see we have declared two variables, x and y, which are considered as operands with values 5 and 3. Print("The manipulation after applying not equal to operator on above operands is as follows:") Print("The second operand with its value is as follows:") Print("The first operand with its value is as follows:") Example #1Ĭode: print("Program to demonstrate not equal to (!=) operator is as follows:") Now let us see an example to demonstrate the not equal to the operator (!=). In the above syntax, we saw that we can define “not equal to” in two ways in Python using “!=” or “is not” in the expressions or conditions and returns the Boolean value “True” or “False” having operands with the same type on both sides of the operator. This statement or expression will return Boolean values such as “True” or “False”. Now let us in detail in the below section. Hence the not equal to the operator is a comparison operator and is denoted as “!=”.
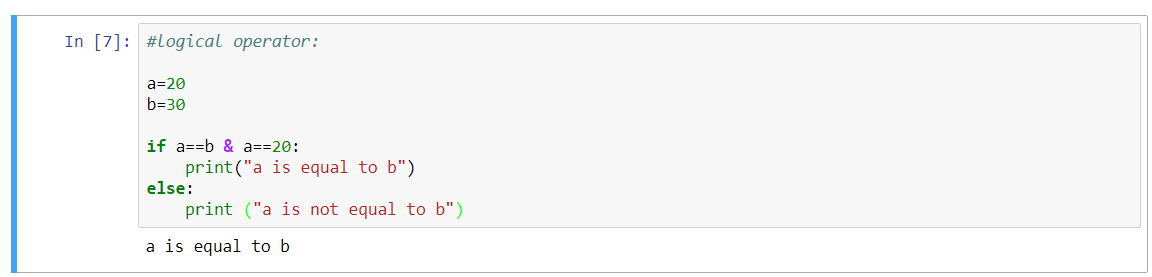
This operator is used to compare the two values, which returns true if both the operand values are not equal at both the side of the operator but have the same type, else it returns false. In this section, we will see the syntax and examples of not equal to the operator in Python. Working of not equal to operator in Python with syntax This returns true when the values of operands on each side do not match or are not equal otherwise, it will return false. This not equal to the operator is exactly the opposite of the equal to the operator.

In Python, the values that this not equal to the operator operates on is known as an operand. This is usually represented as “ != ” and “ is not ” for operating this not equal to operator. This not equal to the operator is a special symbol in Python that can evaluate logical or arithmetic expressions. In general, the operator’s concept in any programming language is used to perform any logical or arithmetic operations on defined variables and their values, and this operator is known as the comparison operator. In this article, we will discuss a Python not equal to an operator. Introduction to Python not equal to operator


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
